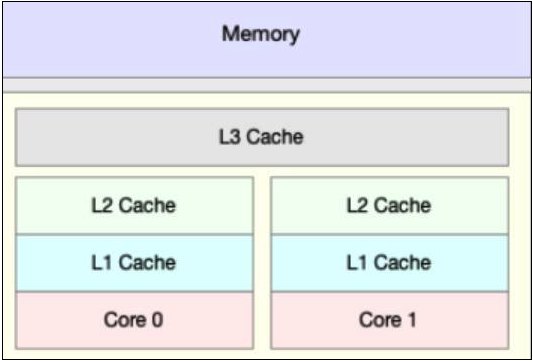
对计算机组成原理相对熟悉的小伙伴都知道,CPU 的速度比内存的速度高了几个数量级,为了 CPU 更快从内存中读取数据,设置了多级缓存机制,如下图所示:

当 CPU 运算时,首先会从 L1 缓存查找所需要的数据,如果没有找到,再去 L2 缓存中去找,以此类推,直到从内存中获取数据,这也就意味着,越长的调用链,所耗费的执行时间也越长。那是不是可以从主内存拿数据的时候,顺便多拿一些呢?这样就可以避免频繁从主内存中获取数据了。聪明的计算机科学家已经想到了这个法子,这就是缓存行的由来。缓存是由多个缓存行组成的,而每个缓存行大小通常来说,大小为 64 字节,并且每个缓存行有效地引用主内存中的一块儿地址,CPU 每次从主内存中获取数据时,会将相邻的数据也一同拉取到缓存行中,这样当 CPU 执行运算时,就大大减少了与主内存的交互。
下面我用一个例子让大家体会一下用缓存行和不用缓存行在性能上的差异:
// 以下源码例子来源:https://tech.meituan.com/2016/11/18/disruptor.html
public class CacheLineEffect {
//考虑一般缓存行大小是64字节,一个 long 类型占8字节
static long[][] arr;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size = 1024 * 1024;
arr = new long[size][];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
arr[i] = new long[8];
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
arr[i][j] = 0L;
}
}
long sum = 0L;
long marked = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
sum = arr[i][j];
}
}
System.out.println("[cache line]Loop times:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - marked) + "ms");
marked = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i += 1) {
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
sum = arr[j][i];
}
}
System.out.println("[no cache line]Loop times:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - marked) + "ms");
}
}
我使用的测试运行环境配置如下:
运行后结果如下:
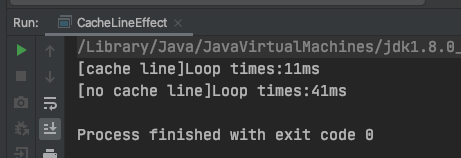
可以看到,使用缓存行比没有使用缓存行的性能提升了将近 4 倍。
当 CPU 执行完后,还需要将数据回写到内存上,以便于别的线程可以从主内存中获取最新的数据。假设两个线程都加载了相同的 Cache line 数据,会产生什么样的影响呢?下面我用一张图解释:
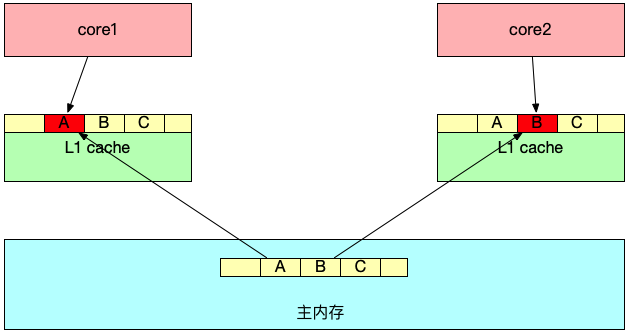
数据 A、B、C 被加载到同一个 Cache line,假设线程 1 在 core1 中修改 A,线程 2 在 core2 中修改 B。
线程 1 首先对 A 进行修改,这时 core1 会告知其它 CPU 核,当前引用同一地址的 Cache line 已经无效,随后 core2 发起修改 B,会导致 core1 将数据回写到主内存中,core2 这时会重新从主内存中读取该 Cache line 数据。
可见,如果同一个 Cache line 的内容被多个线程读取,就会产生相互竞争,频繁回写主内存,降低了性能。
要解决伪共享这个问题最简单的做法就是将线程间共享元素分开到不同的 Cache line 中,这种做法叫用空间换取时间,具体做法如下:
public final static class ValuePadding {
// 前置填充对象
protected long p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7;
// value 值
protected volatile long value = 0L;
// 后置填充对象
protected long p9, p10, p11, p12, p13, p14, p15;
}
JDK1.8 有专门的注解 @Contended 来避免伪共享,为了更加直观,我使用了对象填充的方法,其中 protected long p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7 作为前置填充对象,protected long p9, p10, p11, p12, p13, p14, p15作为后置填充对象,这样任意线程访问 ValuePadding 时,value 都处于不同的 Cache line 中,不会产生伪共享问题。
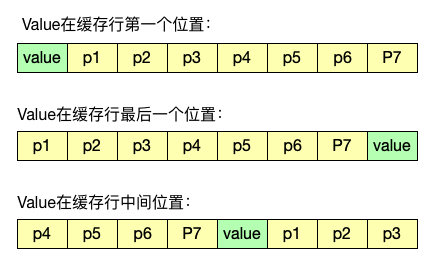
下面的例子用来演示伪共享与解决伪共享后的性能差异:
public class MyFalseSharing {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
System.gc();
final long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
runTest(Type.PADDING, i);
System.out.println("[PADDING]Thread num " + i + " duration = " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
System.gc();
final long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
runTest(Type.NO_PADDING, i);
System.out.println("[NO_PADDING] Thread num " + i + " duration = " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
}
private static void runTest(Type type, int NUM_THREADS) throws InterruptedException {
Thread[] threads = new Thread[NUM_THREADS];
switch (type) {
case PADDING:
DataPadding.longs = new ValuePadding[NUM_THREADS];
for (int i = 0; i < DataPadding.longs.length; i++) {
DataPadding.longs[i] = new ValuePadding();
}
break;
case NO_PADDING:
Data.longs = new ValueNoPadding[NUM_THREADS];
for (int i = 0; i < Data.longs.length; i++) {
Data.longs[i] = new ValueNoPadding();
}
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(new FalseSharing(type, i));
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
t.start();
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
t.join();
}
}
// 线程执行单元
static class FalseSharing implements Runnable {
public final static long ITERATIONS = 500L * 1000L * 100L;
private int arrayIndex;
private Type type;
public FalseSharing(Type type, final int arrayIndex) {
this.arrayIndex = arrayIndex;
this.type = type;
}
public void run() {
long i = ITERATIONS + 1;
// 读取共享变量中指定的下标对象,并对其value变量不断修改
// 由于每次读取数据都会写入缓存行,如果线程间有共享的缓存行数据,就会导致伪共享问题发生
// 如果对象已填充,那么线程每次读取到缓存行中的对象就不会产生伪共享问题
switch (type) {
case NO_PADDING:
while (0 != --i) {
Data.longs[arrayIndex].value = 0L;
}
break;
case PADDING:
while (0 != --i) {
DataPadding.longs[arrayIndex].value = 0L;
}
break;
}
}
}
// 线程间贡献的数据
public final static class Data {
public static ValueNoPadding[] longs;
}
public final static class DataPadding {
public static ValuePadding[] longs;
}
// 使用填充对象
public final static class ValuePadding {
// 前置填充对象
protected long p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6;
// value 值
protected volatile long value = 0L;
// 后置填充对象
protected long p9, p10, p11, p12, p13, p14, p15;
}
// 不填充对象
// @sun.misc.Contended
public final static class ValueNoPadding {
protected volatile long value = 0L;
}
enum Type {
NO_PADDING,
PADDING
}
}
运行程序,测试结果如下:
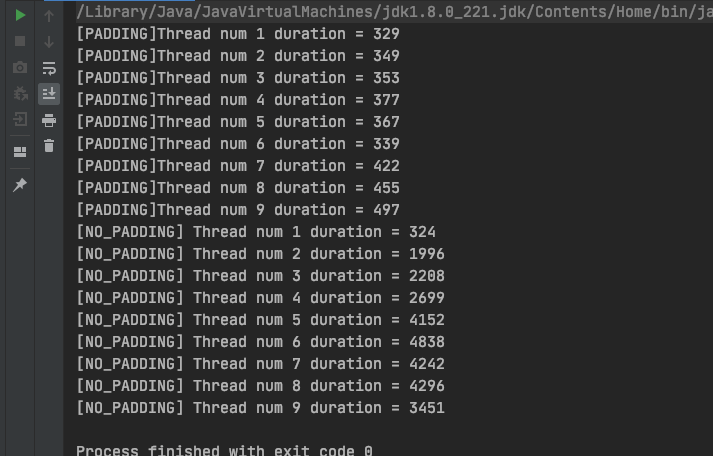
可见,当有多个线程同时操作同一个 Cache line 的数据时,伪共享问题会影响 CPU 性能。