Proxy 类中最重要的一个方法:
Object proxyObject = Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader classLoader, Class[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h);
该方法动态创建实现了 interfaces 数组中所有指定接口的实现类对象。
方法源码:
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
// 检查InvocationHandler不为空,如果为空则抛异常
Objects.requireNonNull(h);
final Class>[] intfs = interfaces.clone();
final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs);
}
// 利用指定类加载器与一组与指定接口相关代理类生成class对象
Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
/*
* Invoke its constructor with the designated invocation handler.
*/
try {
if (sm != null) {
checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl);
}
// 获取代理对象的构造方法 $Proxy0(InvocationHandler h)
final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
final InvocationHandler ih = h;
if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction() {
public Void run() {
cons.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
}
// 生成代理类的实例并把InvocationHandlerImpl的实例传给它的构造方法
return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h});
} catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Throwable t = e.getCause();
if (t instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) t;
} else {
throw new InternalError(t.toString(), t);
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
}
}
InvocationHandler 是代理实例的调用处理程序实现的接口。
每个代理实例都具有一个关联的调用处理程序。对代理实例调用方法时,将对方法调用进行编码并将其指派到它的调用处理程序的 invoke 方法。
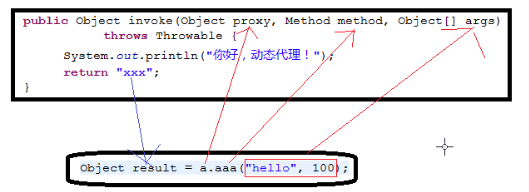
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args);
如下图所示:

定义一个接口:
public interface User {
public void eat();
}
定义一个 Man 类,实现 User 接口:
public Man implements User {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃饭");
}
}
生成动态代理类:
User man = (Man) Proxy.newProxyInstance(User.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{User.class},
(proxy, method, args) -> {
System.out.println("盛饭");
// 调用目标对象的目标方法
method.invoke(proxy, args);
System.out.println("喝水");
});
// 这个方法会依次打印 “盛饭”,“吃饭”,“喝水”
man.eat();