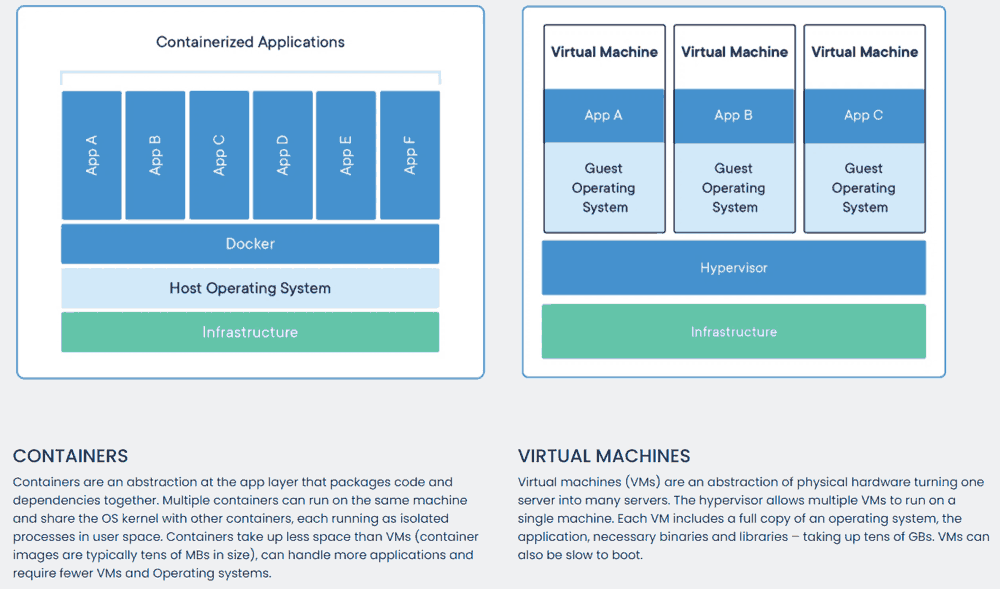
Why did Docker decide to go with a whale for their logo? Apparently to express its product's values of expedition, automation, encapsulation and simplification. As they explain "the whale is carrying a stack of containers on its way to deliver those to you".

下面改编自 官方教程. 总得来说, Dockerfile 类似脚本, 记录了构建镜像 (文件) 的指令. 运行着的镜像称为容器 (类似进程). 而 docker-compose.yml 记录了运行镜像的参数配置 (类似用 shell 脚本记录命令行).
<!-- more -->示例 是 python 的 Flask 应用.
python-docker
|____ app.py
|____ requirements.txt
|____ Dockerfile
Dockerfile 是文本文件, 存储了用 docker build 命令构建 Docker 镜像时的指令. 推荐用默认名 Dockerfile 命名这个文件.
基础镜像.
FROM python:3.8-slim-buster
名字为 -slim 的镜像只装了 minimal packages, 所以用之前记得测试一下.
然后可以写
ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED 1
Setting
PYTHONUNBUFFEREDto a non-empty value different from 0 ensures that the python output i.e. thestdoutandstderrstreams are sent straight to terminal (e.g. your container log) without being first buffered and that you can see the output of your application (e.g. django logs) in real time.
设置 working directory. Docker 后续操作都以 WORKDIR 为默认路径, 使用相对路径即可. 如果 WORKDIR 不存在会自动创建.
WORKDIR /app
复制文件. 第一个参数是本地文件系统中的路径, 第二个参数是 Docker 容器文件系统中的路径 (相对于 WORKDIR).
COPY requirements.txt requirements.txt
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt # 运行命令
COPY . . # 全部复制过去
镜像在容器中运行时, 执行的指令. 只能有一个 CMD. The main purpose of a CMD is to provide defaults for an executing container.
# CMD ["executable","param1","param2"]
CMD ["python3", "-m" , "flask", "run", "--host=0.0.0.0"]
# 主参数是路径, --tag (-t) 给镜像命名 `name:tag`
docker build --tag python-docker .
docker images # 查看所有镜像
# Name components may contain lowercase letters, digits and separators.
# A separator is defined as a period, one or two underscores, or one or more dashes.
# A name component may not start or end with a separator.
docker tag python-docker:latest python-docker:v1.0.0
上述操作导致同一镜像 (相同 image id) 有两个名字, 去掉 (untagged) 一个.
docker rmi python-docker:v1.0.0
A container is a normal operating system process except that this process is isolated in that it has its own file system, its own networking (不能直接通过 localhost 对应端口访问), and its own isolated process tree separate from the host.
在 docker run 命令中加上 --publish (-p).
# [host port]:[container port]
docker run --publish 8000:5000 python-docker
如上容器内暴露的端口是 5000 (Flask 默认), 对应主机 (localhost) 暴露的端口是 8000, 此时才能通过 localhost:8000 访问到.
# 查看容器, 加上 --all (-a) 显示停止的容器
# 返回一张表格, 其中 command 是之前写的 CMD
# ports 列出端口
# names 如果没有给定会随机生成, 比如 funny_brahmagupta
docker ps
# --detach (-d) 后台运行
docker run -d -p 8000:5000 python-docker
# pass the name of the container or the container ID
docker stop funny_brahmagupta
When you restart a container, it starts with the same flags or commands that it was originally started with.
docker restart funny_brahmagupta
docker stop funny_brahmagupta
When you remove a container, it is no longer running, nor it is in the stopped status, but the process inside the container has been stopped and the metadata for the container has been removed.
# 可以传入多个容器
docker rm funny_brahmagupta blahblah
给容器命名.
docker run -d -p 8000:5000 --name rest-server python-docker
创建两个 volumes.
docker volume create mysql
docker volume create mysql_config
docker volume ls
# docker volume rm mysql
Now we'll create a network that our application and database will use to talk to each other. The network is called a user-defined bridge network and gives us a nice DNS lookup service which we can use when creating our connection string.
docker network create mysqlnet
docker run --rm -d -v mysql:/var/lib/mysql \
-v mysql_config:/etc/mysql -p 3306:3306 \
--network mysqlnet \
--name mysqldb \
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=p@ssw0rd1 \
mysql # 镜像名
Now, let's make sure that our MySQL database is running and that we can connect to it.
docker exec -ti mysqldb mysql -u root -p
下面会提示输入密码, 登录 MySQL 数据库. Press CTRL-D to exit the MySQL interactive terminal.
修改了 Python 程序, 见 原文.
docker build --tag python-docker-dev .
docker run \
--rm -d \
--network mysqlnet \
--name rest-server \
-p 8000:5000 \
python-docker-dev
This allows us to access the database by its container name.
用 YAML 文件 docker-compose.dev.yml 存储配置, 不必每次都 docker run 一堆参数.
version: '3.8'
services:
web:
build:
context: .
ports:
- 8000:5000
volumes:
- ./:/app
mysqldb:
image: mysql
ports:
- 3306:3306
environment:
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=p@ssw0rd1
volumes:
- mysql:/var/lib/mysql
- mysql_config:/etc/mysql
volumes:
mysql:
mysql_config:
We expose port 8000 so that we can reach the dev web server inside the container. We also map our local source code into the running container to make changes in our text editor and have those changes picked up in the container.
docker-compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml up --build
# 假设用默认名
docker-compose stop
docker-compose up --build
docker-compose up -d
The Compose file is a YAML file defining version (DEPRECATED), services (REQUIRED), networks, volumes, configs and secrets.
Computing components of an application are defined as Services. Services communicate with each other through Networks. Services store and share (主机和容器共享) persistent data into Volumes. A Secret is a specific flavor of configuration data for sensitive data that SHOULD NOT be exposed without security considerations. Configs 先不管.
services:
web: # 服务的名字, 可以随便起
# specifies the build configuration for creating container image from source
build:
# defines either a path to a directory containing a Dockerfile
# When the value supplied is a relative path, it MUST be interpreted as relative to the Compose file’s parent folder.
context: .
ports:
# SHOULD always be specified as a (quoted) string, to avoid conflicts with yaml base-60 float. 下面加上双引号了.
# 其他例子: "127.0.0.1:5000-5010:5000-5010" 加上 IP 和端口 range.
- "8000:5000"
volumes:
# VOLUME:CONTAINER_PATH
# VOLUME: MAY be either a host path on the platform
# hosting containers (bind mount) or a volume name
- ./:/app
# 环境变量
environment:
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=p@ssw0rd1
# container's network stack is not isolated from the Docker host (the container shares the host's networking namespace), and the container does not get its own IP-address allocated. 如果用 host, 则前面的 ports 端口映射也不再适用.
network_mode: host
其中 build 可以写为
build: .
To reuse a volume across multiple services, a named volume MUST be declared in the top-level volumes key.
...
volumes:
- mysql:/var/lib/mysql
- mysql_config:/etc/mysql
volumes:
mysql:
mysql_config:
上述例子没指定主机路径则默认挂载到 /var/lib/docker/volumes/...
Best practices for writing Dockerfiles
Because an image is built during the final stage of the build process, you can minimize image layers by leveraging build cache.
For example, if your build contains several layers, you can order them from the less frequently changed (to ensure the build cache is reusable) to the more frequently changed:
依赖相比其他项目代码更不容易改变, 因此先复制 requirements.txt 安装依赖, 再把其他代码拷贝到容器里.